About cookies on this site Our websites require some cookies to function properly (required). In addition, other cookies may be used with your consent to analyze site usage, improve the user experience and for advertising. For more information, please review your options. By visiting our website, you agree to our processing of information as described in IBM’sprivacy statement. To provide a smooth navigation, your cookie preferences will be shared across the IBM web domains listed here.
Abstract
IBM® MessageSight is an appliance that is designed for the Internet of Things (IoT) and mobile environments. It provides a secure, DMZ-ready channel for lightweight, rapid, bidirectional messaging. MessageSight offers mobile application support, handles massive scaling of concurrent device connectivity and communication, and offers high-performance messaging. The appliance is DMZ ready and allows organizations to securely extend the messaging enterprise to external clients and sensors. It can act as the gateway for business data flowing in and out of the enterprise’s network. MessageSight is developer friendly and is designed for easy deployment and integration.
This IBM Redbooks® Solution Guide explains how to implement real-time mobile application solutions using MessageSight. It includes a scenario that shows how a taxi company developed a PickMeUp mobile application that integrated MessageSight and MQTT.
Contents
IBM® MessageSight is an appliance that is designed for the Internet of Things (IoT) and mobile environments. It provides a secure, DMZ-ready channel for lightweight, rapid, bidirectional messaging. MessageSight offers mobile application support, handles massive scaling of concurrent device connectivity and communication, and offers high-performance messaging. The appliance is DMZ ready and allows organizations to securely extend the messaging enterprise to external clients and sensors. It can act as the gateway for business data flowing in and out of the enterprise’s network. MessageSight is developer friendly and is designed for easy deployment and integration.
This IBM Redbooks® Solution Guide explains how to implement real-time mobile application solutions using MessageSight. It includes a scenario that shows how a taxi company developed a PickMeUp mobile application that integrated MessageSight and MQTT.
Figure 1 illustrates how clients who are connected to MessageSight can interface with back-end applications. It also shows how MessageSight connects many users and devices on the Internet to services that are deployed on an intranet. The users, devices, sensors, and services interact with each other by exchanging messages through MessageSight.
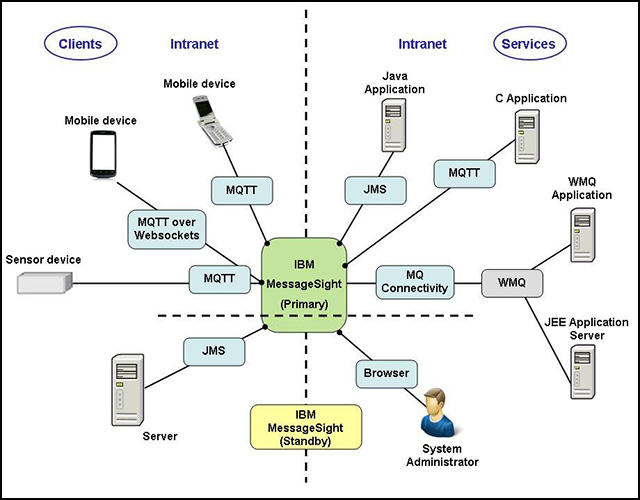
Figure 1. Typical IBM MessageSight connectivity design
Did you know?
One MessageSight appliance can serve up to a million devices connected concurrently and can handle the throughput of up to 13 million nonpersistent messages or 400,000 persistent messages per second with predictable latency in microseconds under load.
Business value
By processing large volumes of events in near real time, MessageSight delivers the performance, value, and simplicity that organizations need to accommodate the ever growing multitude of mobile devices and sensors. MessageSight extends messaging networks with extreme transaction rates, massive scale, and predictable low latency. It delivers messaging for the edge of the enterprise to reach out to the expanding IoT, the dramatic scaling in the number of concurrent devices that can be connected with timely information.
These capabilities allow today's organizations to be more engaged to support new systems of interaction with clients, partners, and employees by unlocking information in systems of record to enable business to be conducted anywhere. Unlike messaging appliances that merely consolidate traditional messaging services onto a hardware form factor, MessageSight is specifically engineered to deliver massive scale communications within and beyond the enterprise. It is designed with specific optimization to accelerate reliable messaging delivery with persistence qualities minimizing latency, and provide high and predictable throughput.
In real time, MessageSight supports new levels of performance and scale across a wide variety of use cases that include massive sensor networks, intelligent automotive applications, and large-scale mobile banking. By scaling huge numbers of concurrently connected devices, the appliance enables large volumes of events to be streamed into analytic engines for processing big data.
Solution overview
A taxi company wants to improve its quality of service and productivity by automating its business processes. They can do this by taking advantage of mobile technologies. They want to connect a passenger who needs a taxi with one of the company's taxi drivers and to do so in the most convenient and effective way possible. The traditional, centralized call center model is not efficient in many cases, because there can be delays or errors at the coordinator end that can lead to unexpected mishaps between a passenger and driver. This taxi company wants to develop a PickMeUp mobile application for taxi drivers and for passengers by using a real-time engagement that can be established between the passenger and driver.
A passenger using the PickMeUp mobile application can perform following actions:
Others who read this also read
Special Notices
The material included in this document is in DRAFT form and is provided 'as is' without warranty of any kind. IBM is not responsible for the accuracy or completeness of the material, and may update the document at any time. The final, published document may not include any, or all, of the material included herein. Client assumes all risks associated with Client's use of this document.
