Abstract
The IBM® Worklight mobile application platform helps organizations develop, deploy, host, and manage mobile enterprise applications. IBM Worklight provides tools for every stage of the mobile application development and deployment process. In addition, IBM Worklight integrates security into the entire mobile application lifecycle. Therefore, the IBM Worklight platform is composed of five main components, which provide a flexible and robust solution for mobile application security. This IBM Redbooks Solution Guide describes the architecture, integration, and use cases of adopting IBM Worklight for mobile security.
Contents
IBM® Worklight mobile application platform helps organizations develop, deploy, host, and manage mobile enterprise applications. IBM Worklight provides tools for every stage of the mobile application development and deployment process. In addition, IBM Worklight integrates security into the entire mobile application lifecycle. As shown in Figure 1, the IBM Worklight platform is composed of the five main components: Worklight Studio, Application Center, Device Runtime, Server, and Console, which provide a flexible and robust solution for mobile application security.

Figure 1. Main components of the IBM Worklight platform
Did you know?
The Worklight security framework does not include its own user registry, credentials storage, or access control management. Instead, it delegates all those functions to the existing enterprise security infrastructure. The delegation allows the Worklight server to integrate as a presentation tier into the existing enterprise landscape and supports custom extensions that allow integration with any security mechanism.
Business value
When extending their business to mobile platforms, enterprises need a rich development environment so their applications can run on various mobile operating systems, including Android, BlackBerry, iOS, and Windows Phone. They also must determine the application type they adopt: web, native, hybrid, or a combined approach.
Enterprises must also tackle the following major mobile security threats:
IBM Worklight supports multiple operating systems and devices with the simplicity of a single, shared code base. It can also be used in all mobile application types. Moreover, IBM Worklight safeguards mobile security at the device, application, and network layer:
Solution overview
Figure 2 shows the mapping of mobile security objectives and IBM Worklight security capabilities, which are described in this section.
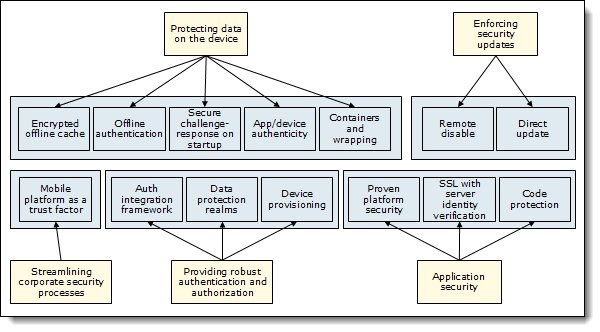
Figure 2. The mapping of Worklight security capabilities to mobile security objectives
Protecting data on the device
On-device storage of data can be tampered with by malware on the device; if the device is lost or stolen, sensitive data can be extracted by unauthorized third parties. Worklight provides the following capabilities to protect data on the device:
Securing the application
IBM Worklight protects the application and prevents hackers from unpackaging the legitimate mobile application and repackaging it with malicious code:
Enforcing security updates
Worklight offers the direct update and remote disable features to help administrators ensure that critical updates to their applications are delivered in a timely manner:
Providing robust authentication and authorization
Worklight provides the following features for authentication and authorization:
Streamlining corporate security processes
IBM Worklight integrates with existing protocols to streamline and augment the existing security process. Applications that are built using Worklight are trusted entities that adhere to corporate security policies. The result is a quicker approval process, faster time to market, and increased confidence that risks are being mitigated.
Solution architecture
This section outlines the solution architecture for using Worklight for mobile security.
Security components
Figure 3 shows the security components of IBM Worklight, the corresponding security features, and Worklight’s integration with web gateways.
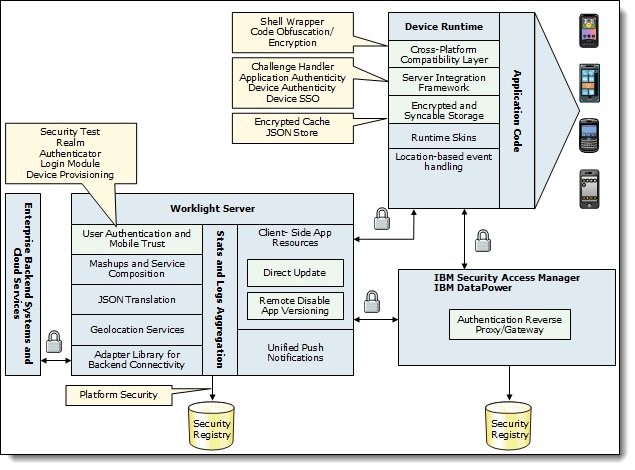
Figure 3. Worklight security components
Framework overview
The IBM Worklight security framework serves two main goals:
The Worklight security framework supports multi-factor authentication. This means that any protected resource can require multiple checks to control access. A protected resource can be an application, an adapter procedure, an event source, or a static resource. A typical example of multi-factor authentication is the combination of device, application, and user authentication.
Authentication architecture
Each type of security check has its own configuration, and a configured check is called a realm. Multiple realms can be grouped in a named entity that is called a security test. The realms are defined in the authentication configuration file on the Worklight project level. A realm consists of two parts:
Each security check defines its own protocol, which is a sequence of challenges that are sent by the server and responses that are sent by the client:
The Worklight security framework provides a wire protocol that allows for a combination of challenges and responses for multiple security checks to be included in a single request-and-response round trip. The protocol serves two important purposes:
Figure 4 shows the Worklight authentication architecture.
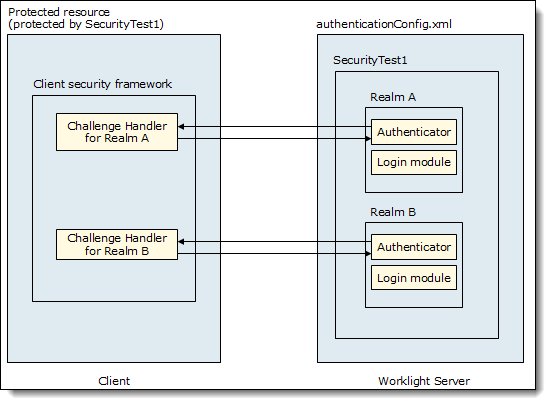
Figure 4. Worklight authentication architecture
Authentication flow
Here is the authentication flow in Worklight:
Usage scenarios
IBM Worklight solutions expand a broad range of industries and organizations. Use cases apply to financial institutions, healthcare, education, computer services, retail, and more.
Financial institutions
In this scenario, the fictional Banking Company A selects IBM Worklight as its mobile application platform. Banking Company A wants to build a secure platform, increase staff productivity, ensure secure and easy access for customers, and accelerate development and deployment.
Building a secure platform
Increasing staff productivity
Ensuring secure and easy access for customers
Accelerating development and deployment
Healthcare
In this scenario, the fictional Hospital B also chooses IBM Worklight as its mobile application platform. Hospital B wants to build a secure platform, increase responsiveness and perceived value perception, and reduce multi-platform development costs.
Building a secure platform
Increasing responsiveness and perceived value perception
Reducing multi-platform development costs
Integration
This section introduces two ways in which Worklight can integrate with other security solutions.
Integration with container security
Worklight Server is technically a web application that is hosted by an application server. Therefore, it is desirable to reuse the authentication capabilities of the application server for Worklight Server, and vice versa. To understand the differences between Worklight and web container authentication models, consider the following items:
As a result, the authentication integration between Worklight Server and the Java Platform, Enterprise Edition container is implemented as a custom Worklight realm. This realm can interact with the container and obtain and set its authenticated principal. Worklight Server includes a set of login modules and authenticators for WebSphere Application Server Full Profile and WebSphere Application Server Liberty Profile that implement this integration with LTPA tokens.
Integration with web gateways
Web gateways such as IBM WebSphere DataPower® and IBM Security Access Manager (ISAM) provide user authentication so that only authenticated requests can reach the internal applications. The internal applications can obtain the result of the authentication that is performed by the gateway from a special header. Adding a web gateway to the Worklight deployment provides leading practice defense in-depth protection by authenticating clients in the DMZ and can add features such as content acceleration, scalability, and high availability with load balancing, content inspection, and risk based access.
When Worklight Server is protected by a web gateway, the client requests first encounter the gateway. The gateway sends back an authentication challenge and validates the credentials, and if the validation is successful, submits the request to the Worklight Server. This sequence implies the following requirements on the Worklight security elements:
Supported platforms
IBM Worklight runs on the following operating systems:
For more information about the software and hardware requirements of IBM Worklight, see System Requirements for IBM Worklight and IBM Mobile Foundation, found at http://www.ibm.com/support/docview.wss?uid=swg27024838.
Ordering information
Ordering information is show in Table 1.
Table 1. Ordering part numbers and feature codes
Related information
For more information about IBM Worklight, see the following documents:
On this page, enter IBM Worklight, select the information type, and then click Search. On the next page, narrow your search results by geography and language.

Figure 1. Main components of the IBM Worklight platform
Did you know?
The Worklight security framework does not include its own user registry, credentials storage, or access control management. Instead, it delegates all those functions to the existing enterprise security infrastructure. The delegation allows the Worklight server to integrate as a presentation tier into the existing enterprise landscape and supports custom extensions that allow integration with any security mechanism.
Business value
When extending their business to mobile platforms, enterprises need a rich development environment so their applications can run on various mobile operating systems, including Android, BlackBerry, iOS, and Windows Phone. They also must determine the application type they adopt: web, native, hybrid, or a combined approach.
Enterprises must also tackle the following major mobile security threats:
- Loss and theft
- Malware
- Spam
- Phishing
- Bluetooth and Wi-Fi
IBM Worklight supports multiple operating systems and devices with the simplicity of a single, shared code base. It can also be used in all mobile application types. Moreover, IBM Worklight safeguards mobile security at the device, application, and network layer:
- Protects sensitive information from malware attacks and device theft
- Ensures timely propagation and adoption of critical security updates to the entire installation base
- Enforces multi-factor authentication, single sign-on (SSO), and device SSO while integrating with existing authentication and security approaches
- Enables secure delivery and operation of mobile apps for employee-owned devices or device types that are not allowed on the corporate network
- Manages approved and rejected devices for controlled mobile-application installation and remote application disablement
Solution overview
Figure 2 shows the mapping of mobile security objectives and IBM Worklight security capabilities, which are described in this section.

Figure 2. The mapping of Worklight security capabilities to mobile security objectives
Protecting data on the device
On-device storage of data can be tampered with by malware on the device; if the device is lost or stolen, sensitive data can be extracted by unauthorized third parties. Worklight provides the following capabilities to protect data on the device:
- Encrypted offline cache
Worklight encrypts data on the device by using advanced encryption standards (AES) and public-key cryptography standards (PCKS). The data can be stored on the device as a cache or in the Worklight mobile storage JSONStore.
Offline authentication
When applications are running on mobile devices that are not connected to the network, the need for user authentication still exists. The encrypted cache feature in Worklight can be used to achieve more offline authentication because only the correct passwords can unlock the offline cache.
Secure challenge-response on startup
Worklight provides extended authentication with a server by using secure challenges and responses.
Application and device authenticity
Worklight provides application and device authenticity to ensure that only valid applications on authorized mobile devices can be used. Worklight generates a unique identification for the application and the device, and protects them from tampering by using digital signatures. Whenever the application tries to access back-end systems through the Worklight server, the server verifies the application authenticity and device authenticity if activated and allows access only from legitimate applications.
Securing the application
IBM Worklight protects the application and prevents hackers from unpackaging the legitimate mobile application and repackaging it with malicious code:
- Proven platform security
IBM Worklight has security mechanisms that are deployed by enterprises with extreme security requirements, such as top-tier financial institutions. Running IBM Worklight on IBM WebSphere® Application Server further strengthens its security features with those provided by WebSphere Application Server.
SSL with server identity verification
IBM Worklight enables a security-rich client and server communication over HTTPS to prevent data leakage and to prevent automatic server certificate verification to thwart known attacks, such as man-in-the-middle attack.
Code protection
Worklight provides capabilities to obfuscate and encrypt the application code and web resources to prevent tampering of the application.
Enforcing security updates
Worklight offers the direct update and remote disable features to help administrators ensure that critical updates to their applications are delivered in a timely manner:
- Direct update
The direct update feature enables developers to drive updates of the web content of the deployed HTML5 and hybrid applications directly from the Worklight Server upon application start.
Remote disable
The remote disable feature provides administrators with the ability to disable the old version of the application for situations in which the distribution of a security fix requires that users get the new application version from the application store.
Providing robust authentication and authorization
Worklight provides the following features for authentication and authorization:
- Authentication integration framework
Worklight provides a server-side architecture that integrates with a back-end authentication infrastructure that is based on JAAS with authentication realms and a client-side framework or asynchronous login requests on session expiration.
Data protection realm
In Worklight, resources are protected by authentication realms. When a user attempts to access a protected resource, Worklight checks whether the user is already authenticated according to the process that is defined for the realm of the resource. If the user is not authenticated, Worklight triggers the challenge-response process of obtaining the client credentials and verifying them as defined in the realm.
Device provisioning
Worklight offers the device provisioning feature to validate device identities. Device IDs are used to identify unique devices with the Worklight server. A certificate must be created that is handled by an external trusted authority, which enhances security by signing the key pair.
Streamlining corporate security processes
IBM Worklight integrates with existing protocols to streamline and augment the existing security process. Applications that are built using Worklight are trusted entities that adhere to corporate security policies. The result is a quicker approval process, faster time to market, and increased confidence that risks are being mitigated.
Solution architecture
This section outlines the solution architecture for using Worklight for mobile security.
Security components
Figure 3 shows the security components of IBM Worklight, the corresponding security features, and Worklight’s integration with web gateways.

Figure 3. Worklight security components
Framework overview
The IBM Worklight security framework serves two main goals:
- Controls access to the protected resources.
- Propagates the user or server identity to the back-end systems through the adapter framework.
The Worklight security framework supports multi-factor authentication. This means that any protected resource can require multiple checks to control access. A protected resource can be an application, an adapter procedure, an event source, or a static resource. A typical example of multi-factor authentication is the combination of device, application, and user authentication.
Authentication architecture
Each type of security check has its own configuration, and a configured check is called a realm. Multiple realms can be grouped in a named entity that is called a security test. The realms are defined in the authentication configuration file on the Worklight project level. A realm consists of two parts:
- The authenticator: Obtains the credentials from the client.
- The login module: Validates the credentials and builds the user identity.
Each security check defines its own protocol, which is a sequence of challenges that are sent by the server and responses that are sent by the client:
- On the server side, the component that implements this private protocol is the authenticator.
- On the client side, the corresponding component is called the challenge handler.
The Worklight security framework provides a wire protocol that allows for a combination of challenges and responses for multiple security checks to be included in a single request-and-response round trip. The protocol serves two important purposes:
- Minimizes the number of extra round trips between the client and the server.
- Separates the application business logic from the security check implementation.
Figure 4 shows the Worklight authentication architecture.

Figure 4. Worklight authentication architecture
Authentication flow
Here is the authentication flow in Worklight:
- When the client request tries to access a protected resource, the Worklight Server checks all the appropriate realms that are specified in the defined security test. One or more realms can decide to send a challenge to the client. Challenges from multiple realms are composed into a single response and sent back to the client.
- The Worklight client security framework extracts the individual challenges from the response and routes them to the appropriate challenge handlers that are defined in the mobile application code.
- When a challenge handler finishes the processing, it submits its response to the Worklight client security framework. When all the responses are received, the Worklight client security framework resends the original request with all the challenge responses.
- The Worklight Server extracts those responses from the request and passes them to the appropriate authenticators. If an authenticator is satisfied, it reports a success and the Worklight Server calls the login module. If the login module succeeds in validating all of the credentials, the realm is considered successfully authenticated.
- If all the realms of the security test are successfully authenticated, the Worklight Server allows the request processing to proceed.
- If a realm check fails, its authenticator sends another or the same challenge to the client and the whole security challenge-response process repeats itself.
Usage scenarios
IBM Worklight solutions expand a broad range of industries and organizations. Use cases apply to financial institutions, healthcare, education, computer services, retail, and more.
Financial institutions
In this scenario, the fictional Banking Company A selects IBM Worklight as its mobile application platform. Banking Company A wants to build a secure platform, increase staff productivity, ensure secure and easy access for customers, and accelerate development and deployment.
Building a secure platform
- Using IBM Worklight, Banking Company A is able to take advantage of its existing security system. Worklight integrates with the company’s existing directories, data stores, and authentication mechanism.
- On the application level, Worklight enforces application updates in a timely manner and controls the authenticity of the applications on user devices.
- For on-device data, Worklight helps Banking Company A protect sensitive information from malware attacks and device theft by using AES256 and PCKS#5 encryption.
Increasing staff productivity
- Employees at Banking Company A can perform daily tasks, such as balance inquiries and loan approvals, on mobile devices. Exceptional tasks, such as approving a loan after hours or from outside the office, require a second authority to verify the transaction approval.
- Banking Company A provides corporate-owned devices and also facilitate Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) (where it is approved for its employees).
Ensuring secure and easy access for customers
- Some customers of Banking Company A use both the mobile banking application and the stock trading application. The single sign-on feature of Worklight enables customers to start the other application if they are authenticated with one application already.
- Banking Company A wants to implement an additional authentication for high-value transactions of customers. It chooses to integrate Worklight with IBM Security Access Manager. Without required changes for the application, the company can add additional fraud detection systems to validate the location of the device and the time that the transaction is occurring.
- With the device provisioning and application authenticity features of Worklight, customers of Banking Company A have the liberty of registering multiple devices and disabling a device temporarily or permanently.
Accelerating development and deployment
- Banking Company A uses IBM Worklight Studio to develop multi-platform applications so that its applications are consumable by most of its customers.
- As part of end-to-end security and vulnerability testing, Banking Company A employs the capabilities of the IBM Security AppScan® suite to ensure endpoint security for their web-based systems and to perform static analysis on their mobile application source code.
- Banking Company A uses IBM Worklight Console to collect and analyze user statistics. Banking Company A can collect and analyze security-related data, including actual usage patterns, identify compromised or jail broken devices, and rapidly deploy new applications for testing and solicit and map feedback on its applications.
Healthcare
In this scenario, the fictional Hospital B also chooses IBM Worklight as its mobile application platform. Hospital B wants to build a secure platform, increase responsiveness and perceived value perception, and reduce multi-platform development costs.
Building a secure platform
- IBM Worklight provides an extensible authentication model as part of its function. To comply with the Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS), Hospital B uses Worklight with WebSphere Application Server for added protection. The hospital configures WebSphere Application Server to protect the application and adapters that are hosted on the IBM Worklight runtime environment.
- Using Worklight, Hospital B is able to grant access to data on a role, time, and location basis. Doctors can access patient records on mobile devices. However, it requires an additional authentication approval if they are at home or on call to review the latest observations of patients. In addition, although doctors have access to the information of their patients, medical suppliers have access to check inventory and update stock.
Increasing responsiveness and perceived value perception
- Hospital B is looking for a communication solution to find employees anywhere in the hospital. Using Worklight, the hospital can build an application that allows instant and secure communication. Doctors and nurses can quickly find colleagues without stopping what they are doing.
- Doctors at Hospital B must input prescriptions when their mobile devices are not connected to the network. JSONStore, the document-oriented storage system in Worklight, ensures that the documents in the application are always available to doctors even when the devices running the application are offline. JSONStore also provides AES 256 encryption of confidential health information.
- With the application, patients can pre-register for appointments and input their allergies and health history using mobile devices. Worklight uses Secure Sockets Layer with server identity verification and enables communication over HTTPS to protect the information.
Reducing multi-platform development costs
- IBM Worklight provides a standards-based platform and allows Hospital B to use third-party libraries and frameworks.
- Using Worklight, Hospital B can also create mobile applications quickly by using any combination of HTML5, native, and hybrid development methods.
Integration
This section introduces two ways in which Worklight can integrate with other security solutions.
Integration with container security
Worklight Server is technically a web application that is hosted by an application server. Therefore, it is desirable to reuse the authentication capabilities of the application server for Worklight Server, and vice versa. To understand the differences between Worklight and web container authentication models, consider the following items:
- The Java Platform, Enterprise Edition model allows only one authentication scheme for a web application, with multiple resource collections that are defined by URL patterns with authentication constraints defined by a white list of role names.
- The Worklight model allows protection of each resource by multiple authentication checks, and the resources are not necessarily identified by the URL pattern. In some cases, authentication can be triggered dynamically during the request processing.
As a result, the authentication integration between Worklight Server and the Java Platform, Enterprise Edition container is implemented as a custom Worklight realm. This realm can interact with the container and obtain and set its authenticated principal. Worklight Server includes a set of login modules and authenticators for WebSphere Application Server Full Profile and WebSphere Application Server Liberty Profile that implement this integration with LTPA tokens.
Integration with web gateways
Web gateways such as IBM WebSphere DataPower® and IBM Security Access Manager (ISAM) provide user authentication so that only authenticated requests can reach the internal applications. The internal applications can obtain the result of the authentication that is performed by the gateway from a special header. Adding a web gateway to the Worklight deployment provides leading practice defense in-depth protection by authenticating clients in the DMZ and can add features such as content acceleration, scalability, and high availability with load balancing, content inspection, and risk based access.
When Worklight Server is protected by a web gateway, the client requests first encounter the gateway. The gateway sends back an authentication challenge and validates the credentials, and if the validation is successful, submits the request to the Worklight Server. This sequence implies the following requirements on the Worklight security elements:
- The client-side challenge handler must be able to present the gateway's login mechanism, submit the credentials, and recognize the login failure and success.
- The authentication configuration must include the realm that can obtain and validate the token that is provided by the gateway.
- The security test configuration must take into account that the user authentication is always performed first.
Supported platforms
IBM Worklight runs on the following operating systems:
- IBM AIX®
- HP-UX
- Linux
- Mac OS
- Mobile OS
- Solaris
- Windows
For more information about the software and hardware requirements of IBM Worklight, see System Requirements for IBM Worklight and IBM Mobile Foundation, found at http://www.ibm.com/support/docview.wss?uid=swg27024838.
Ordering information
Ordering information is show in Table 1.
Table 1. Ordering part numbers and feature codes
| Program name | PID number |
| IBM Worklight | 5725-I43 |
| IBM WebSphere Application Server | 5724-J08 |
| IBM WebSphere DataPower Service Gateway XG45 | 7198-32X |
| IBM WebSphere DataPower Integration Appliance XI52 | 7199-42X |
| IBM Security Access Manager | 5725-C87 |
Related information
For more information about IBM Worklight, see the following documents:
- Securing Your Mobile Business with IBM Worklight, SG24-8179
- IBM Worklight product page
- IBM Worklight V6.0 - technology overview
- IBM Worklight V6.0 information center
- IBM Worklight V6.0 data sheet
- IBM Offering Information page (to search on announcement letters, sales manuals, or both):
http://www.redbooks.ibm.com/redpieces/abstracts/sg248179.html?Open
http://www.ibm.com/software/products/us/en/worklight/
http://www.ibm.com/common/ssi/ShowDoc.wss?docURL=/common/ssi/ecm/en/wsw14181usen/index.html&lang=en&request_locale=en
http://pic.dhe.ibm.com/infocenter/wrklight/v6r0m0/index.jsp
http://public.dhe.ibm.com/common/ssi/ecm/en/wsd14109usen/WSD14109USEN.PDF
http://www.ibm.com/common/ssi/index.wss?request_locale=en
On this page, enter IBM Worklight, select the information type, and then click Search. On the next page, narrow your search results by geography and language.
Others who read this also read
Special Notices
The material included in this document is in DRAFT form and is provided 'as is' without warranty of any kind. IBM is not responsible for the accuracy or completeness of the material, and may update the document at any time. The final, published document may not include any, or all, of the material included herein. Client assumes all risks associated with Client's use of this document.
