Abstract
Business process management (BPM) solutions enable an enterprise to choreograph processes and the process steps across disparate applications, people, and systems. In addition to reduced cost through continued process improvement and automation, BPM provides the foundation for converged and agile business and IT responsiveness.
The benefits of implementing BPM solutions using IBM Business Process Manager are presented in this IBM® Redbooks® Solution Guide.
Contents
Business process management (BPM) solutions enable an enterprise to choreograph processes and the process steps across disparate applications, people, and systems. In addition to reduced cost through continued process improvement and automation, BPM provides the foundation for converged and agile business and IT responsiveness. Figure 1 illustrates the concepts of the BPM discipline.
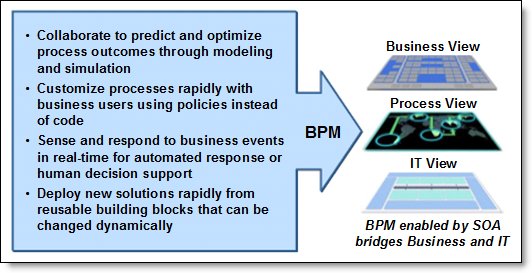
Figure 1. BPM drives business and IT alignment and responsiveness
Did you know?
The basic principals of business process management—that a process can be broken into distinct operations, with each operation performed by a role—was famously documented in the 18th century by Scottish moral philosopher Adam Smith. Smith described the production of a pin, breaking down the tasks to make a pin head into eighteen distinct operations.
Business value
The notion of process optimization gained prominence during the Industrial Revolution through “specialization.” Thought leaders worked on streamlining their processes for producing goods in order to get more to markets at lower cost. In the industrialized world economy, business leaders have recently started embracing an enhanced version of this concept because they need help to manage the interactions between systems and humans. This discipline is BPM.
The key distinction between BPM and process optimization is BPM's added focus on flexible and dynamic process design, process orchestration, and automation through IT enablement. In addition to reducing costs through continued process improvement and automation, BPM provides the foundation for converged and agile business and IT responsiveness. Business leaders today look to it to help them get their goods and services to market better, faster, and cheaper than their competitors.
Intrinsic to BPM is the principle of continuous operational improvement, perpetually increasing value generation and sustaining market competitiveness or dominance. BPM focuses on driving overall bottom-line success by integrating business verticals and optimizing core work (for example, order-to-cash, integrated product development, and integrated supply chain). This focus helps direct the deployment of resources throughout the organization into efficient processes that create customer value—which differentiates BPM from traditional (that is, compartmentalized) functional management disciplines.
Others who read this also read
Special Notices
The material included in this document is in DRAFT form and is provided 'as is' without warranty of any kind. IBM is not responsible for the accuracy or completeness of the material, and may update the document at any time. The final, published document may not include any, or all, of the material included herein. Client assumes all risks associated with Client's use of this document.
